Written by Dentistry TodayTuesday, 03 January 2012 12:09
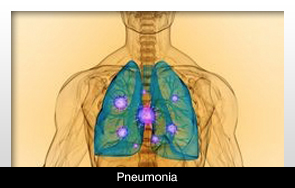
There may be a connection between poor oral health and pneumonia, according to Yale University.
The study shows that changes in the mouth resulting from bacteria could lead to pneumonia, according to Dr. Samit Joshi from the Yale University School of Medicine. Older people are also at a higher risk of developing pneumonia.
The study involved 37 participants who were analyzed throughout the course of a month. The research indicated that people who were on ventilators who developed pneumonia went through a major change to their oral bacteria before becoming sick.
The connection between illnesses involving the respiratory system and oral health has been discussed for years. The reason is bacterial infections in the chest stem from breathing droplets from the mouth and throat that seep into the lungs. Also, the more gum issues a person has, the greater the chance of death from pneumonia.
Basic dental care and maintaining good oral health can make the connection between oral bacteria and pneumonia irrelevant to a person.
This information could eventually be beneficial to the way pneumonia is treated